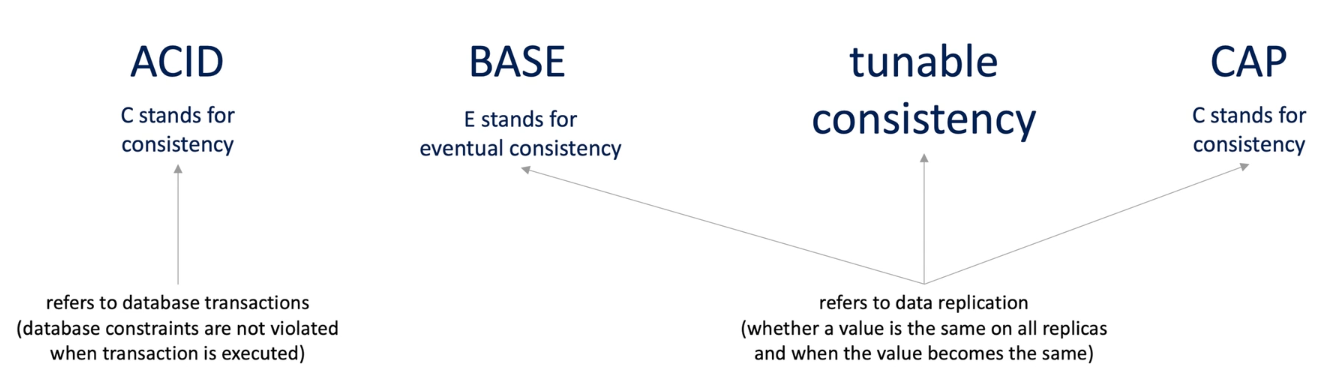
2.8 Consistency
Strong Consistency (changes are reflected to all users immeidately) vs Weak Consistency (changes take some time to reach all users because there're different versions of the data in the system)
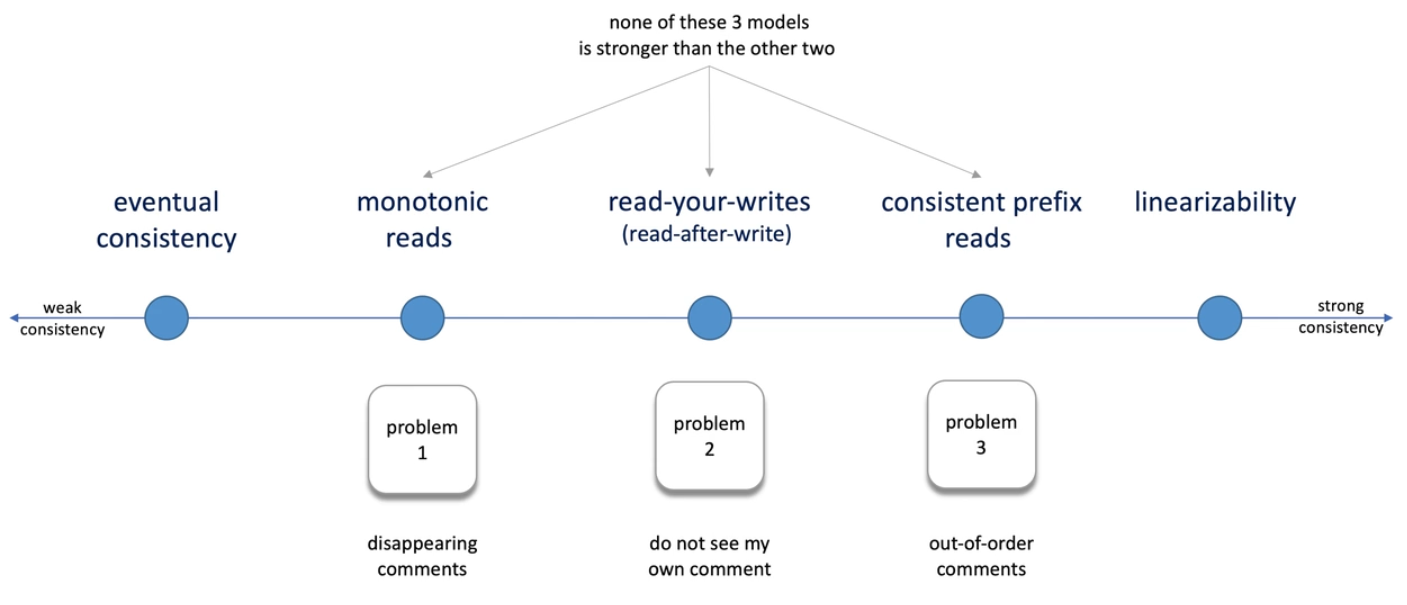
We need some terminologies in the middle: Consistency Models
Linearizability Consistency Model
When updates are completed, all clients will get the updated value when they read it.
Drawbacks:
- It is slow
- when there is a network partition, linearizability and availability are mutually exclusive
Typical usage: banking, e-commerce, booking systems, distributed locks
Eventual Consistency Model
If there are no additional updates made to the object, eventaully all reads will return the latest written value of that object. It does not guarantee when exactly replication will complete.
Inconsistency window is typically small (sub-second)
Can be much faster than linearizability
No need to sacrifice availability
DNS is the most popular example
Drawbacks:
- May cause a lot of confusion
Monotonic Reads Consistency Model
Read-Your-Writes Consistency Model
Consistent Prefix Reads Consistency Model