Fundamentals and High Level Overview
System Design Process
- Gather requirments
- Back of envelope calculations
- API design
- Architectual design
1 Database
- sequential reads and writes are always cheaper than random reads and writes
- want to keep data that is frequently read together close together
- want to keep data that is frequently written to together close together
- indexes can be used to speed up reads, but often at the expense of slowing down writes
- without index, we can just write data sequentially, that is basically a WAL (Write Ahead Log), but reads will be slow: O(n)
1.1 Hash Index
- reads and writes are O(1)
- usually in memory
- range query is impossible, because each data is written into random memory/disk addresses, they're not sequential, so range query is essentailly N reads, where N is the size of the range
1.2 B+ Tree Index
- tree structure allows for O(log n) read speed
- data are written together on disk (for primary keys), so range query is fast
- for indexes other than primary keys, range query is also fast because the pointers to the range data are stored together (the leaves of the B+ tree)
- but data on disk are stored sequentially according to the primary key, not second indexes
- which means even though pointers are used for fast query reads, but the actual data are scattered around the disk, so querying is still not as efficient as primary key index
1.3 LSM Tree Index (Memtable + SSTables)
-
writes are fast because they're written to the memtable in memory first
-
memtable itself is also a tree - self balanced binary tree
-
data in memtable is being flushed to disk periodically as SSTables
-
SSTables are compacted into a new SSTable for the next layer to reduce the size because only the latest update for a key is relevant and stored
-
read is slow, because it requires a linear scan (O(n)) of all the memtable and SSTables until the key is found
- if a key is really really old, at worst case scenario, all SSTables would need to be scaned to find that key
ACID Principle
-
Atomicity: the entire transaction happens at once, or doesn't happen at all
-
Consistency: database must be consistent before and after transactions (follow all rules, no violations)
-
Isoluation: multiple transactions can occur independently without inteference
-
Durability: changes of a successful transaction occurs even if the system failure occurs
-
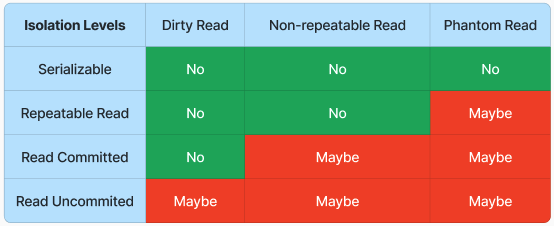
Isolation Levels
- Dirty Read: read the updated value in a transaction that hasn't been commited yet
- Non-repeatable Read: during the course of a transaction, data in a row changes
- Phantom Read: two identical queries return different results (a new row has just been added by another transaction)
- MySQL is repeatable read, PostgreSQL is read commited
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GAe5oB742dw
Bloom Filter
- in situations where read is not efficient (like a LSM tree), use bloom filter can eliminate some of the non-existing keys, thus return "no, key is not there" to save read time.
- it may produce falst positives (it says it's there but it is actually not there) because of hash collisions
- How to choose an appropriate size for bloom filter?
- for a chosen expected number of keys and acceptable false positive rates, use this formula:
-
m = -n * log2(p) / (log(2))^2 - n = number of keys
- p = acceptable false positive rates
- m = size of bloom filter in bits
-
- optimal number of hash functions (k):
-
k = (m / n) * log(2)
-
- for a chosen expected number of keys and acceptable false positive rates, use this formula:
C10K problem?
- the challenge of designing and implementing a server that can efficiently handle a large number of concurrent client connections, specifically 10,000.
- solution:
- asynchronous I/O
- Non-Blocking I/O
- Efficient Data Structures
- Connection Pooling
Change Data Capture
- captures changes made within a database
- Implmentations:
- Query based
- Trigger based
- Log based
- Proprietary (developed by database vendor) based
Idempotent
- some operation is idempotent if it always returns the same result.
- Ex, x=5 is idempotent while x++ is not
Thundering Herd problem?
- when a large number of requests try to access a resources in a small time frame due to reasons like cache eviction, hardware restart, etc.
- Flooded backend may further cause system failures
- To mitigate this issue
- randomized cache expiration time
- rate limiting
- backend sharding
- asynchronous cache updates
- backoff time on client side
Gossip Protocol
- a protocol to detect node failures in a distributed and de-centralized cluster
- each node passes information (heartbeat, timestamp, etc) to a random set of other nodes to let them know its still alive
- other nodes, upon receiving the information, adds information about it self, and pass those information to another set of random nodes
- eventually all nodes will be ping and get the updated information.
- If after a while, all of the nodes haven't heard about one particular node, than that node is considered as down.
- Cassandar uses Gossip Protocol to detect node failures.
123
